Portfolio item number 1
Short description of portfolio item number 1
Short description of portfolio item number 1
Short description of portfolio item number 2 
Published in Paper presented at the ICLR 2020 Workshop on Computer Vision for Agriculture (CV4A), 2020
Machine learning (ML) methods and neural networks (NN) are widely implemented for crop types recognition and classification based on satellite images.
Recommended citation: Matvienko I., et al, 2020 https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.03468
Published in Paper in Eurasian Soil Science, 2020
Interest in studying the effect of commercial humic products (HPs) on the biological activity of soils is dictated by the environmental safety of their use (HPs are produced from natural raw materials), low market value, and high efficiency.
Recommended citation: Pozdnyakov L. A. et al., 2020 https://link.springer.com/article/10.1134/S1064229320050117
Published in Paper presented at the ICCS 2020, 2020
In this research, we perform a sensitivity analysis of soil parameters which play an essential role in plant growth for the MONICA agro-ecosystem model. We utilize Sobol sensitivity indices to estimate the importance of main soil parameters for several crop cultures (soybeans, sugar beet and spring barley).
Recommended citation: Gasanov M., et al, 2020 https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007%2F978-3-030-50436-6_54
Published in Paper presented at the ICCS 2021, 2021
Optimization of water consumption in agriculture is necessary to preserve freshwater reserves and reduce the environment’s burden.
Recommended citation: Gasanov M., et al, 2021 https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-030-77970-2_7
Published in Paper in Nature Communications, 2024
Machine learning-based geospatial applications offer unique opportunities for environmental monitoring due to domains and scales adaptability and computational efficiency
Recommended citation: Koldasbayeva, D., Tregubova, P., Gasanov, M. et al. Challenges in data-driven geospatial modeling for environmental research and practice. Nat Commun 15, 10700 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-55240-8 https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-55240-8
Published:
M. Gasanov, Lomonosov Moscow State University / Soil Science; Y. Leonteva, Lomonosov Moscow State University / Faculty of Soil Science.
Published:
In recent years, there has been growing interest in using humic substances for the purpose of reclamation of contaminated soils and increasing fertility. The appearance of a large number of industrial humic substances (HS) of different in their properties and origin requires the creation of methods for their evaluation. In conditions of high anthropogenic influence, the soils are subjected to complex pollution, trace metals play a significant role in this pollution. The purpose of our research was to evaluate the humic substances in model experiments using microbiological methods. The object of research was sod-podzolic soil, medium loamy. In research, we used three types of HS of various origins: Flexom, Lignohumate and purified humic acids. HS were added at a concentration of 10% and 30% in terms of carbon. Model contaminants for the experiment were lead (Pb) and zinc (Zn), which were introduced in the form of nitrates in a concentration of 540 mg/kg for lead, and 880 mg/kg for zinc. After the incubation of the soil with heavy metals and HS for 3 weeks, microbiological indices and chemical indices of heavy metals in various forms of mobility were measured. To assess the functioning of soils, the characteristics of the soil microbial community were chosen: the carbon content of the microbial biomass and the CO2 emission, due to microbial heterotrophic respiration. According to many researchers, these indicators give a good assessment of the state of microorganisms in the soil. For statistical data processing principal component analysis (PCA) was used. 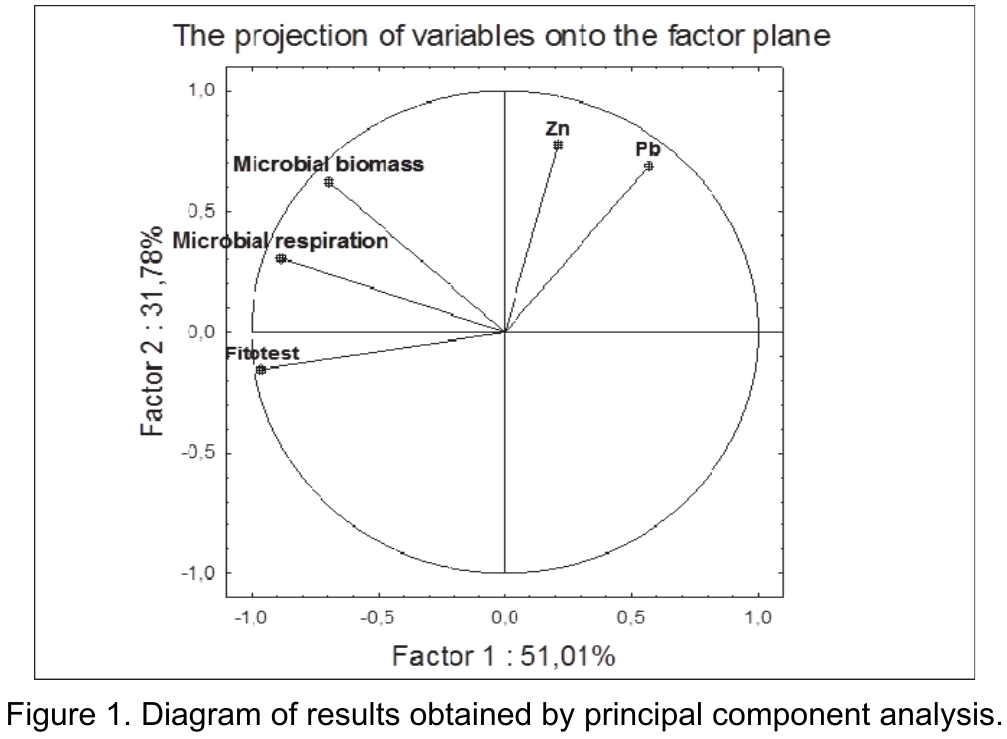
Published:
The necessity for intensification of agriculture in densely populated areas of South-East Asia leads to the active use of fertilizers and pesticides. For the pest management of rice farms, farmers often use neonicotinoids. It is known that humic substances (HS) affect the behavior of organic pollutants in the environment. HS can bind toxicants, changing their migration ability, and provide a stimulating effect on the soil microbial community, accelerating the decomposition process of organic pollutants. 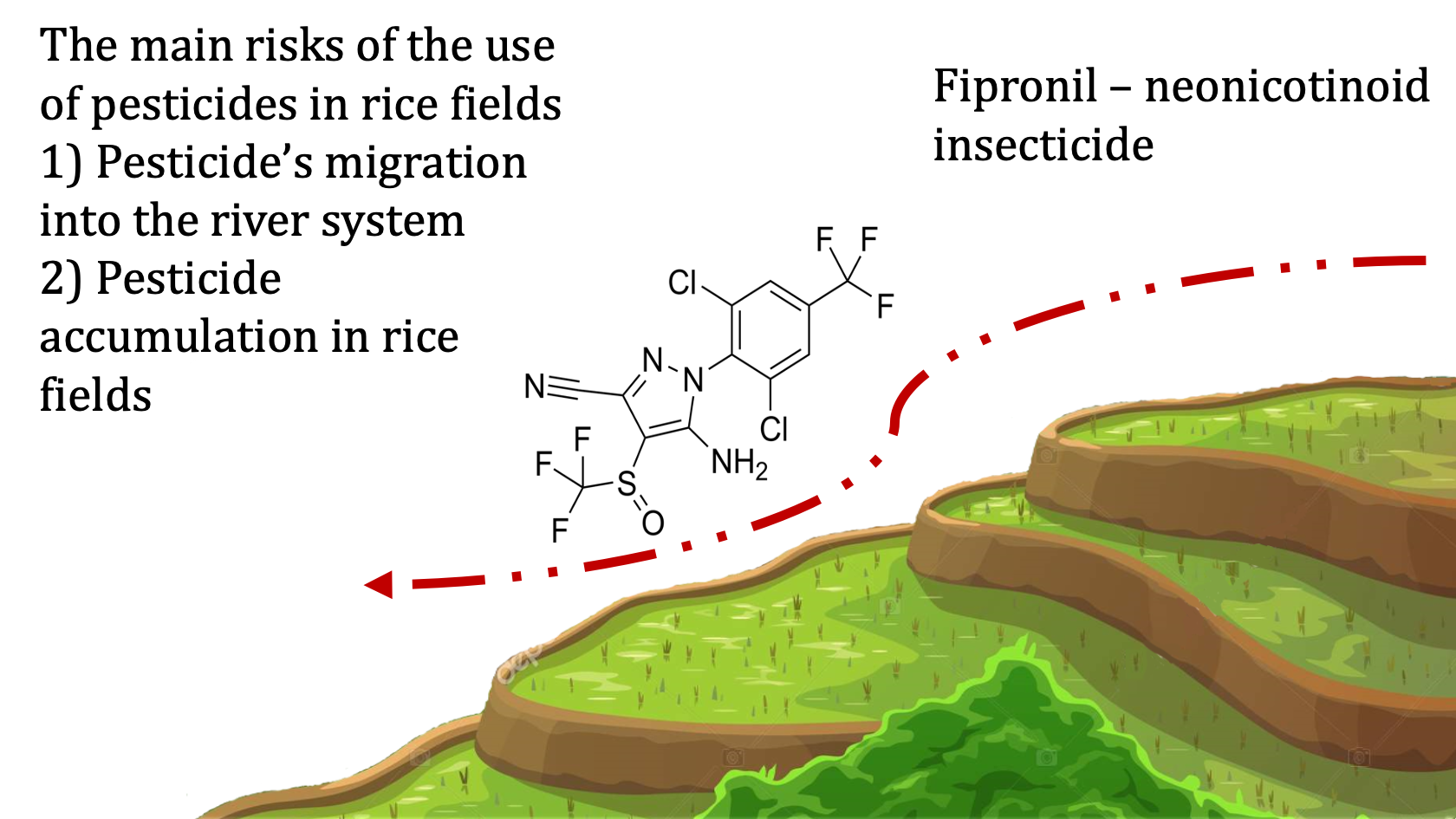
Master student courses, Skoltech, CDISE, 2020
This course covered several milestone problems for future agriculture, like:
Master student courses, Skoltech, Cdise, 2020
Notion course page Link